Rebar Splicing and Overlapping — ACI 318-19 Requirements Explained
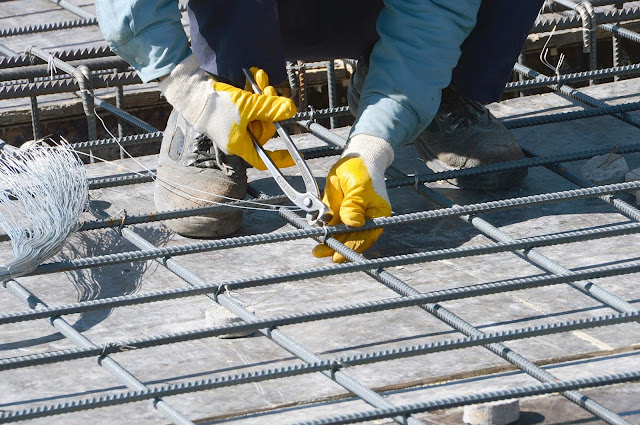
Reinforcement splicing or overlapping is a fundamental requirement in reinforced concrete structures. Because reinforcement bars (rebars) are manufactured in limited standard lengths—typically 12 m—it becomes necessary to splice or overlap them to achieve the required continuity in structural members.
The main purpose of a splice is to ensure smooth stress transfer between adjacent bars through the surrounding concrete. The overlap length, commonly known as the splice length, must be long enough to safely transfer the tensile stresses from steel to concrete without causing bond failure.
It is recommended to avoid splicing in high-stress zones such as areas of maximum moment, and to stagger the splices to prevent congestion and reduce stress concentration.
The ACI 318-19 providing the following recommendatin and requirement for the lap splicing:
1. Splice Limitation by Bar Size
Lap splicing is not permitted for reinforcement bars larger than 36 mm in diameter.
2. Non-Contact Lap Splice in Flexural Members
For non-contact lap splices, the center-to-center spacing between spliced bars shall not exceed the lesser of:
-
one-fifth of the required lap splice length (ℓ<sub>st</sub>), or
-
150 mm.
3. Bundled Bars
When bars are bundled, the splice length shall be increased by:
-
20 % for a three-bar bundle, or
-
33 % for a four-bar bundle.
Each bundle’s splice is based on the development length of the individual bar within the bundle.
4. Lap Splice for Bars in Tension
The required lap splice length, ℓst is derived from the development length (ℓd) and the provisions of ACI Table 25.5.2.1.
6- If bars of different size are lap spliced in tension, ℓst shall be the greater of ℓd of the larger bar and ℓst of the smaller bar.
7-lap splice for bars in compression for bar dia 36 or less shall be calculated in accordance:
a-for fy<=420 Mpa, Lsc is the longer of 0.071*fy*db and 300mm
b-for 420 MPa<fy<=550Mpa, LSC is the longer of (0.13fy-24)db and 300 mm.
c-for fy>550 Mpa, Lsc is the longer of (0.13fy-24)db and Lst calculated in accordance with above table: 25.5.2.1
8-compression lap splics shall not be used for bars larger than db>36mm.
9-Where bars of different size are lap spliced in compression, ℓsc shall be the longer of ℓdc of larger bar and ℓsc of smaller bar calculated in accordance with point no:07 as appropriate.
development length for bar in compression, Ldc shall be the greater of:
a-greater of:
Example 1: Determine the lap splice for a 32 mm and 25mm bar
bundled in 3 bars, in tension zone, bottom layer reinforcement,
uncoated reinforcement, 50% staggered, Asprovided/Arequired<2.0, fy=500 Mpa, fc’=50 Mpa?
So we need to Lst for the greater bar and Ld for the larger
bar
Let determine Ld for 32mm, 25mm
So Ld=25mm
So Ld=32mm
Now let find Lst for greater bar
Lst=1530+300 (from table 25.5.2.1)=1830 mm
So Lst=1830, for bar bundled in 3, the
length will increased by 20%,
So splice length =1.2*1830=2196 mm=2.196
m





















Comments
Post a Comment