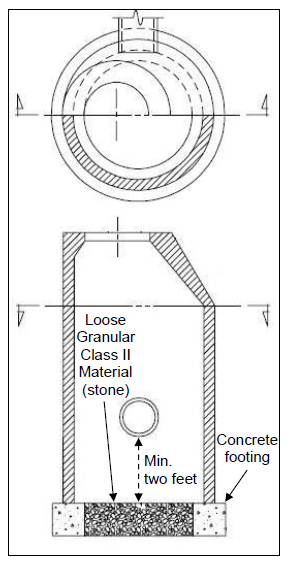
Los Angeles abrasion test

Los Angeles abrasion test conducted to measure the resistance of aggregates to deterioration by impact, abrasion and grinding. The deterioration due to impact, abrasion, and grinding determined by measuring the percentage of wear due to relative rubbing action between aggregates and steel balls inside a drum rotating at a specific speed. the test apparatus includes balance, sieves (80, 63, 50, 40, 25, 20, 12.5, 10, 6.3, 4.75 (as per gradation of aggregate) and 1.7 mm), Los Angeles abrasion machine and abrasion charges. Figure 1 Figure 2 Test procedure · the grade of aggregates will be determined by the sieving of the aggregate sample. The table no:1 shows the different grades of aggregate according to gradation. Table 1 · The test sample shall be clean and dried in an oven at 105 to 110 c˚. The grading of the aggregate shall conform to one of the grading shown in table no:1. The grading of aggregates shall be similar to the g