Causes of Damage to Concrete-Excess Concrete Mix Water
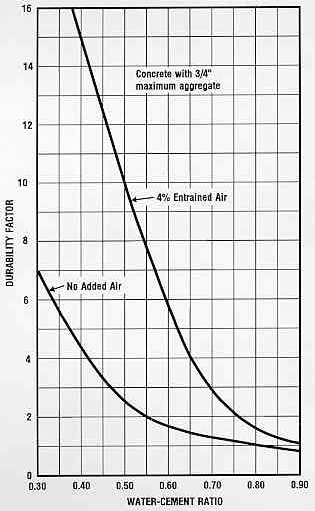
The using of excessive water in the concrete mix will significantly reduce the strength of concrete. High w/c for a concrete mix will result in lowering concrete mixture durability, increase shrinkage, increasing porosity, increasing creep, and reducing abrasion resistance of concrete. Figure no:1 shows the effects of the water-cement ratio on concrete durability. We notice that increasing of the water-cement ratio will reduce the durability of concrete significantly. The high water-cement ratio will increase concrete porosity, which facilitates the ingress of aggressive chemicals such as chloride and sulfate. The presence of chloride will cause steel reinforcement to rust, which causes concrete to cracks. High durable concrete is associated with a low water-cement ratio and the use of air-entrained admixture.
Detecting excess concrete mix water as a cause of concrete damage is difficult. Excess concrete mix water will not appear as the main reason for concrete damage. Excess concrete mix water will be masked by other concrete damages such as Freezing and thawing cracking, abrasion erosion, or drying shrinkage. These causes of concrete damage can be blamed as the primary reason for concrete deterioration without sorting out the main cause. The excess water will lower the durability of concrete that allows for other causes to damage concrete. Petrographic examination (petrographic testing is the use of microscopes to examine concrete samples) can detect the extreme case of excessive water in concrete. The excessive mix of water in hardened concrete can be determined by the presence of bleeding channels or water pockets under large aggregates.
The only permanent repairing of concrete with excessive water mix is the replacement. However, if the extent of damage is shallow (1.5 in, 40 mm), the surface of concrete can be sealed to prevent the penetration of water into concrete service. The prevention of water from penetrating concrete will protect concrete from freezing-thawing cycles and from the ingress of aggressive chemicals such as chloride. Concrete sealing systems require reapplication in an interval of 5 to 10 years.
Figure 1
Detecting excess concrete mix water as a cause of concrete damage is difficult. Excess concrete mix water will not appear as the main reason for concrete damage. Excess concrete mix water will be masked by other concrete damages such as Freezing and thawing cracking, abrasion erosion, or drying shrinkage. These causes of concrete damage can be blamed as the primary reason for concrete deterioration without sorting out the main cause. The excess water will lower the durability of concrete that allows for other causes to damage concrete. Petrographic examination (petrographic testing is the use of microscopes to examine concrete samples) can detect the extreme case of excessive water in concrete. The excessive mix of water in hardened concrete can be determined by the presence of bleeding channels or water pockets under large aggregates.
The only permanent repairing of concrete with excessive water mix is the replacement. However, if the extent of damage is shallow (1.5 in, 40 mm), the surface of concrete can be sealed to prevent the penetration of water into concrete service. The prevention of water from penetrating concrete will protect concrete from freezing-thawing cycles and from the ingress of aggressive chemicals such as chloride. Concrete sealing systems require reapplication in an interval of 5 to 10 years.














Comments
Post a Comment