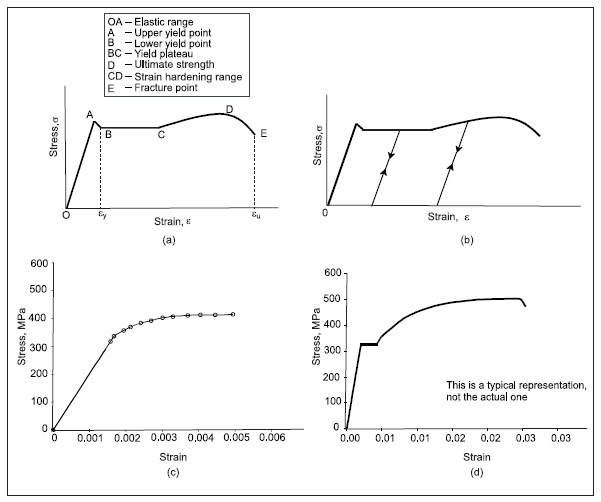
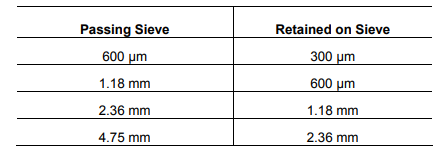
Glass fiber-reinforced polymer

Glass fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP) reinforcement has emerged as a new opponent to conventional reinforcement. The GFRP owns a higher tensile strength, non-corrosive reinforcement, lighter weight, and higher strength-weight ratio. The corrosion of reinforcement can severely damage the structure by causing the concrete to cracks or spall. The Maintainance of damaged structures can significantly be costly. The GFRP is a non-corrosive reinforcement. Therefore, the use of GFRP can eliminate the deterioration of structure due to reinforcement corrosion. The use of GFRP has increased recently for many applications such as bridge deck, pavement, walls, and other applications. However, the use of GFRP is limited due to the lack of information about the long-term performance of GFRP. Figure 1 GRFP bars have many advantages, such as tensile strength. The tensile strength of GRFP bars is higher than the conventional reinforcement. Table no:1 shows the mechanical properties of GRFP bars. We ca